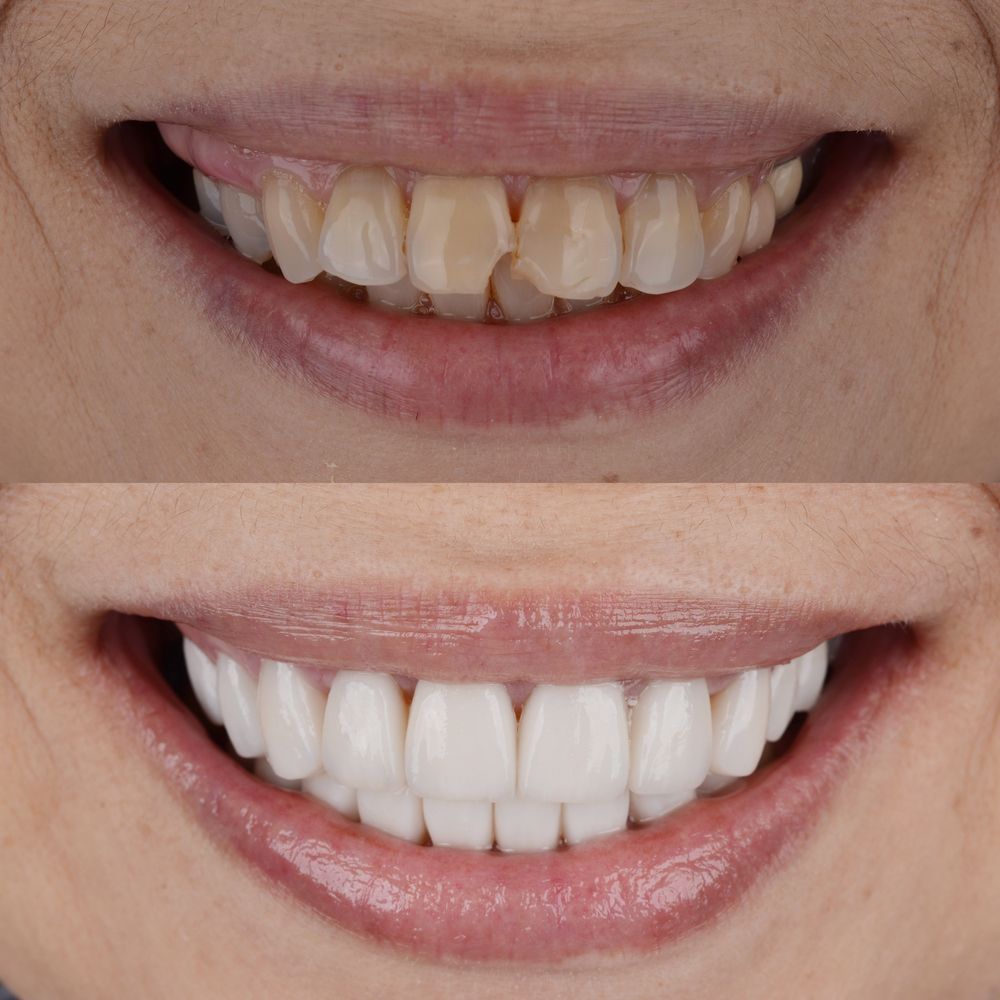
In the ever-evolving field of cosmetic dentistry, dental bonding stands out as a versatile and transformative procedure. Traditionally used to repair chipped, cracked, or discolored teeth, dental bonding has undergone significant advancements, making it an even more powerful tool for enhancing smiles. These innovations have not only improved the durability and aesthetics of bonded teeth but have also made the procedure more efficient and comfortable for patients. This blog delves into the latest breakthroughs in dental bonding techniques, showcasing how these advancements are revolutionizing cosmetic dentistry and offering patients more natural and long-lasting results.
In This Blog:
- Understanding Dental Bonding
- Traditional Dental Bonding Techniques
- Recent Innovations in Dental Bonding Techniques
Understanding Dental Bonding: Definition and Purpose
Dental bonding is a cosmetic dental procedure that involves the application of a tooth-colored resin material to the surface of the teeth. This resin is meticulously shaped and polished to match the surrounding teeth, resulting in a natural and seamless appearance. The bonding process typically involves etching the tooth surface with a mild acid to create a rough texture, which helps the resin adhere better. Once the resin is applied, it is hardened using a special light, usually ultraviolet, which bonds the material to the tooth.
Common Uses of Dental Bonding in Cosmetic Dentistry
Dental bonding is a versatile technique used to address a variety of cosmetic dental issues:
- Repairing Chipped or Cracked Teeth: Bonding is an excellent solution for fixing minor chips and cracks, restoring the tooth’s integrity and appearance.
- Improving the Appearance of Discolored Teeth: For teeth that are stained or discolored and resistant to whitening treatments, bonding can provide a fresh, uniform look.
- Closing Gaps Between Teeth: Bonding can effectively close small gaps or spaces between teeth, enhancing the overall smile.
- Lengthening Teeth: For patients with teeth that are shorter than average, bonding can add length and create a more balanced smile.
Dental bonding is particularly valued for its minimally invasive nature. Unlike other cosmetic procedures such as veneers or crowns, bonding usually requires little to no removal of the natural tooth structure. This preserves the integrity of the tooth while still achieving the desired cosmetic improvement. Furthermore, dental bonding is relatively quick, often completed in a single visit, and is typically less expensive than other cosmetic treatments, making it an accessible option for many patients seeking to enhance their smiles.
Traditional Dental Bonding Techniques
Dental bonding has been a cornerstone of cosmetic dentistry for many years, providing a reliable and effective means to enhance the appearance and function of teeth. The traditional techniques used in dental bonding can be broadly categorized into direct composite bonding and adhesive bonding.
Direct Composite Bonding
Direct composite bonding involves the application of a tooth-colored resin directly to the tooth’s surface. The process begins with the preparation of the tooth, which includes cleaning and lightly etching the surface to ensure better adhesion of the bonding material. A conditioning liquid is then applied to further enhance the bond. The composite resin, selected to match the natural color of the patient’s teeth, is carefully applied, molded, and sculpted to the desired shape. Once the resin is in place, a curing light is used to harden the material, and the bonded area is polished to blend seamlessly with the surrounding teeth. This technique is highly effective for repairing minor chips and cracks, filling small cavities, and reshaping teeth.
Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding, on the other hand, is primarily used for attaching dental restorations such as crowns, veneers, or bridges. This technique involves a multi-step process where a special adhesive is applied to both the tooth and the restoration. The adhesive creates a strong bond between the tooth and the restoration, ensuring stability and longevity. The process typically includes the use of a bonding agent that is light-cured to enhance its adhesive properties. The restoration is then placed on the prepared tooth, and any excess bonding material is removed before the final curing and polishing steps. Adhesive bonding is known for its strength and durability, making it ideal for more extensive dental repairs and restorations.
Recent Innovations in Dental Bonding Techniques
The field of dental bonding has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, driven by technological innovations and material science. These innovations have significantly improved the effectiveness, durability, and aesthetic outcomes of dental bonding procedures.
Advanced Composite Resins
One of the most notable innovations is the development of advanced composite resins. These new materials are stronger, more durable, and more resistant to staining compared to traditional composites. They also provide a more natural appearance, closely mimicking the translucency and luster of natural teeth.
Nanotechnology in Bonding Agents
Nanotechnology has revolutionized bonding agents by incorporating nano-sized particles into the adhesive materials. These particles enhance the bonding strength, reduce microleakage, and minimize post-operative sensitivity. The result is a stronger and longer-lasting bond between the resin and the tooth surface.
Laser-Assisted Dental Bonding
Laser technology has made dental bonding procedures more precise and less invasive. Laser-assisted bonding allows for more accurate shaping and sculpting of the bonding material, leading to better aesthetic results. Additionally, the use of lasers can reduce the need for anesthesia and minimize patient discomfort during the procedure.
3D Printing and CAD/CAM Technology
The integration of 3D printing and CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology has transformed dental bonding. These technologies enable the creation of custom-made bonding solutions that fit perfectly and look natural. The precision offered by CAD/CAM and 3D printing results in faster procedures and more accurate outcomes, enhancing both the functionality and appearance of bonded teeth.
These recent innovations have expanded the capabilities of dental bonding, making it an even more attractive option for patients seeking cosmetic dental improvements. With these advancements, dental bonding can now offer stronger, more aesthetically pleasing, and longer-lasting results.
Conclusion
The advancements in dental bonding techniques have revolutionized the field of cosmetic dentistry, providing patients with more durable, aesthetically pleasing, and comfortable options for enhancing their smiles. From stronger composite resins and nanotechnology-enhanced bonding agents to the precision of laser-assisted procedures and the custom solutions offered by 3D printing and CAD/CAM technology, these innovations ensure that dental bonding remains a highly effective and versatile tool for addressing a wide range of cosmetic dental issues. As the technology continues to evolve, patients can look forward to even better outcomes, making dental bonding an increasingly attractive choice for achieving a natural and beautiful smile. Whether you’re looking to repair a chipped tooth, improve the appearance of discolored teeth, or close gaps, exploring these cutting-edge bonding techniques with a skilled dental professional can help you achieve the smile of your dreams.
Dr. Edward Camacho earned his DDS from the University of Texas Health Science Center. He believes in continuing his education and training and that a dentist’s education should never cease. As a result, he has received extensive training in aesthetic dentistry, restorative dentistry, dental implant placement, orthodontics, computerized dentistry, and laser dentistry. Dr. Camacho’s continued education and completed cosmetic procedures has helped him establish himself as one of San Antonio’s leading cosmetic dentists. He has completed thousands of cosmetic procedures over the span of his 40 year career.